A recent preclinical study has identified a potential therapeutic target for Charcot Marie Tooth disease (CMT). Although this research is in relatively early stages, it could help to develop a new treatment.
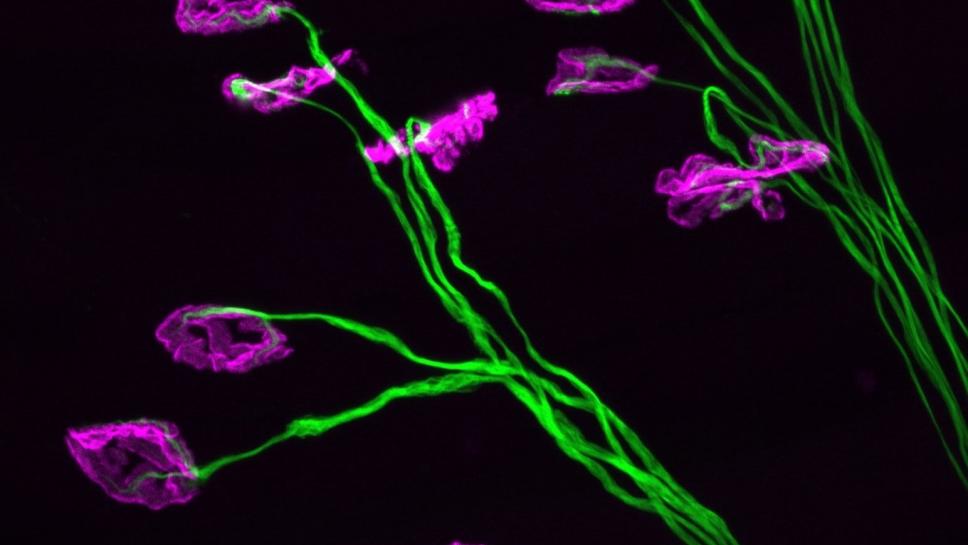
Our nerve cells communicate with other cells by sending electrical signals down their long, thin axons. Within the axons are rod-like structures called microtubules, which act a bit like train tracks. They help to transport cargo, such as proteins, mitochondria and vesicles, up and down the nerve cell (see video below). This process of axonal transport is disrupted in several neurodegenerative conditions, including some types of CMT.
Video illustrating axonal transport, courtesy of Dr James Sleigh at University College London. The bright blue spots are cargoes being moved up and down the nerve cell.
The microtubules in the axon can be modified by a number of proteins, which can impact how well they transport their cargoes. One of these proteins, an enzyme called histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6), has been shown to modify microtubules, leading to impaired axonal transport.
Researchers in the lab of Prof Ludo Van Den Bosch, KU Leuven, previously found that inhibiting these negative effects of HDAC6 improved axonal transport in a mouse model of CMT2F. In this new study, they investigated whether this could also be beneficial to a mouse model of CMT2D.
The researchers treated the CMT2D mice with an HDAC6 inhibitor called tubastatin A. They found that this stabilised the microtubules and improved axonal transport. This improved nerve health, resulting in greater muscle function in the mice.
Lead author of the study, Dr Veronick Benoy, said in a press release:
These results suggest that disturbed acetylation of α-tubulin may be a common hallmark of different forms of CMT. Moreover, we found a cellular link between HDAC6 and the disease-associated protein, indicating that HDAC6 could be linked to CMT disease pathogenesis and that selective inhibition of HDAC6 with a drug could be a beneficial treatment strategy for a wide variety of CMT patients.
This study was published in the scientific journal, Brain.
Further information
Watch Dr Benoy explain some of the study findings
Search for CMT clinical trials
Find out about MDUK-funded CMT research
