Many muscle wasting conditions have a genetic cause, which means that they can be passed down generations (inherited). However not all are inherited in the same way. It’s important to understand what condition you or your family has.
Understanding the role of inheritance and genetics in muscle wasting conditions
If you’re thinking about starting a family, it’s important to understand genetics and typical inheritance patterns as it can tell you about the likelihood of a child being affected or not.
We’d recommend reading this together with our pages relating to your specific muscle wasting condition.
If you have any concerns or questions about inheritance and genetic testing, discuss these with your GP who can refer you to your local genetics counsellor.
What is DNA, chromosomes and genes?
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) contains instructions for the functioning of living organisms. Inside our cells, DNA is organised into structures called chromosomes. These are found in the cell nucleus.
Imagine your DNA as a recipe book, and your genes as the recipes. Our cells use these [genetic] recipes to make proteins, which are essential for a wide range of biological processes in the body.
Almost all our cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes, so 46 in total. These include one pair of sex chromosomes (XX for females, XY for males) and 22 pairs of non-sex chromosomes (autosomes).
For each pair of chromosomes, we inherit one from our mother and one from our father. The rest come from one parent or the other.
For example, some genes involved in energy production are inherited from the mother only. These genes are known to be associated with mitochondrial diseases.
What is a genetic change?
A genetic change is an alteration in the DNA code. This can happen by complete chance, for example if the cell makes a ‘mistake’ during DNA replication.
Sometimes this happens because of environmental factors, such as smoking, excessive exposure to sunlight or exposure to radiation.
Our cells have natural mechanisms for recognising changes and correcting them, but these are not always 100 percent effective.
Depending on where a change occurs, and the type of change it is, the effect could be harmless. Or it could ‘disrupt’ a gene and result in a genetic condition such as muscular dystrophy.
Muscle wasting conditions have different inheritance patterns, depending on the type of condition and which gene has changed.
X- linked recessive inheritance
X-linked recessive inheritance includes but is not limited to:
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Becker muscular dystrophy
- Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy
- X-linked myotubular myopathy (X-MTM)
These conditions are caused by a change in a gene on the X chromosome, which is one of the sex chromosomes. Males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome; females have two X chromosomes.
If a male’s X chromosome has the changed gene, then he will have the condition. He has only one copy of the gene and the change isn’t on the Y chromosome.
If a female has the changed gene on one of her X chromosomes, she still has an unchanged copy of the gene on her other X chromosome. This makes her a ‘carrier’ and she will not usually have symptoms of the condition.
If a carrier of an X-linked condition and a non-carrier have children, there is a 50 percent chance that each son will have the condition and a 50 percent chance that each daughter will be a carrier – as shown in the diagram below.
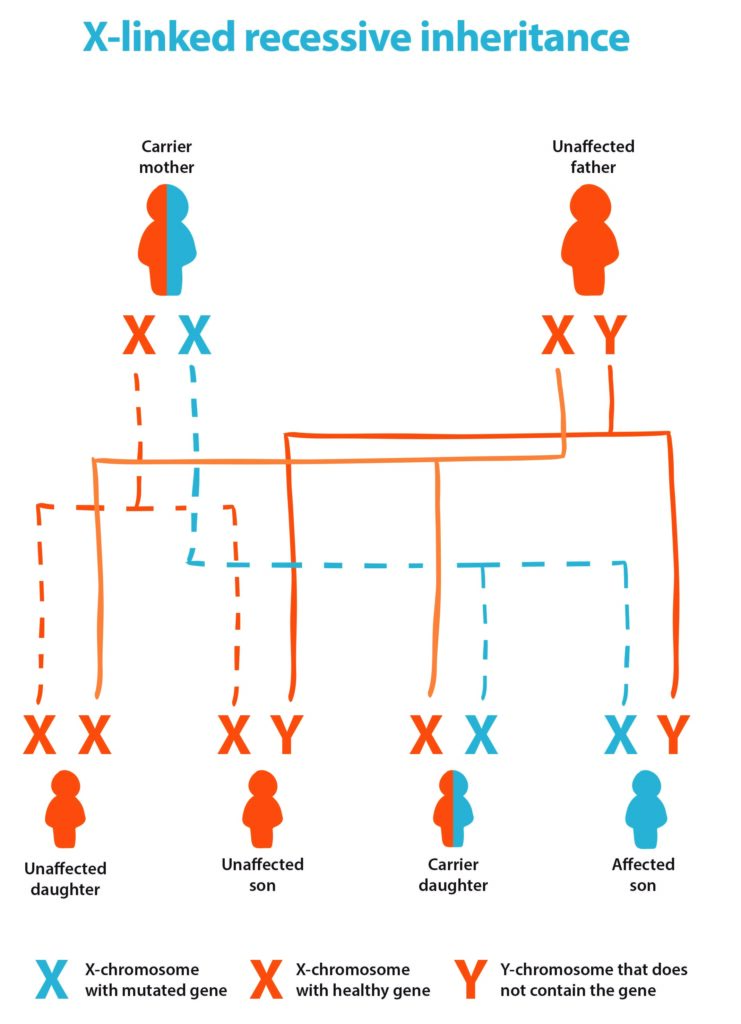
This probability is the same for each child born. So, for instance, if this couple have two sons, each son will have a 50 percent chance of inheriting the condition.
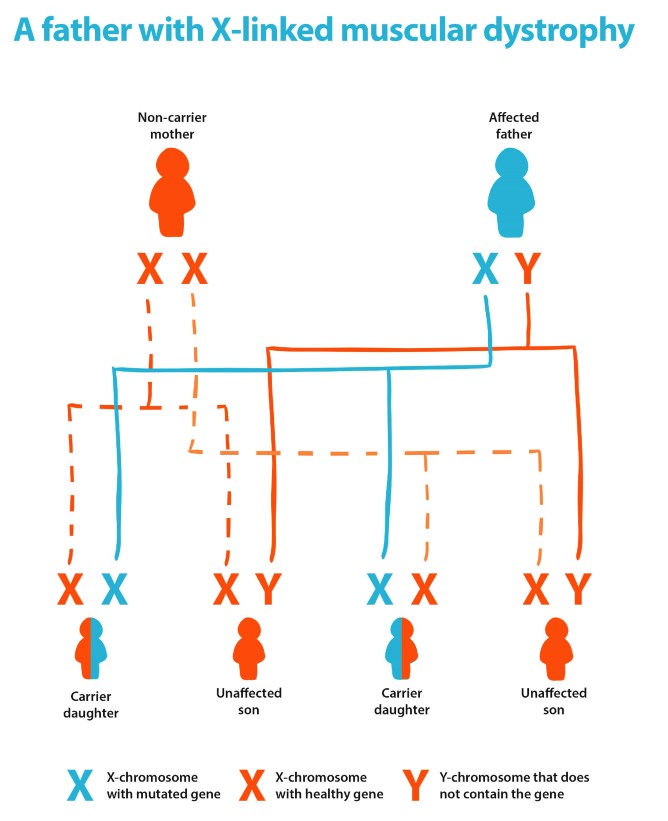
Unaffected males cannot pass on an X-linked condition. Affected males cannot pass an X-linked condition to their sons, but all of their daughters will be carriers – as shown in the diagram below.
Autosomal recessive inheritance
Autosomal recessive inheritance includes, but is not limited to:
- Type 2 limb girdle muscular dystrophies
- Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA)
- Some congenital muscular dystrophies
‘Autosomal’ means the change is in a gene on the non-sex chromosomes, so children of either sex can inherit the condition.
‘Recessive’ means both copies of that gene must be changed for someone to have the condition. If only one copy of the gene has changed, that person is a carrier and will have no symptoms.
If the mother and father are both carriers, as shown in the diagram below, there is a:
- 25 percent chance that each child will be unaffected
- 50 percent chance that each child will be a carrier
- 25 percent chance that each child will have the condition.
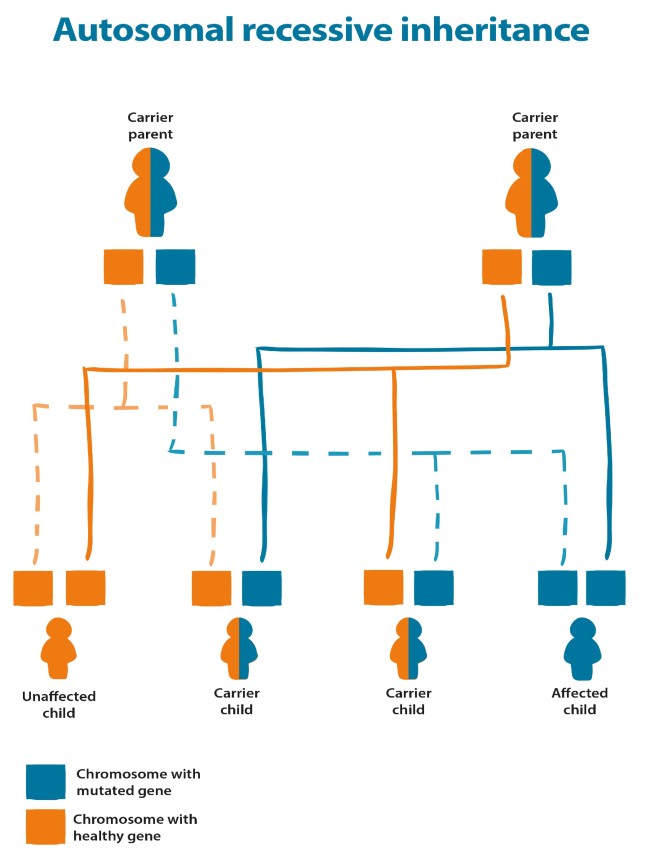
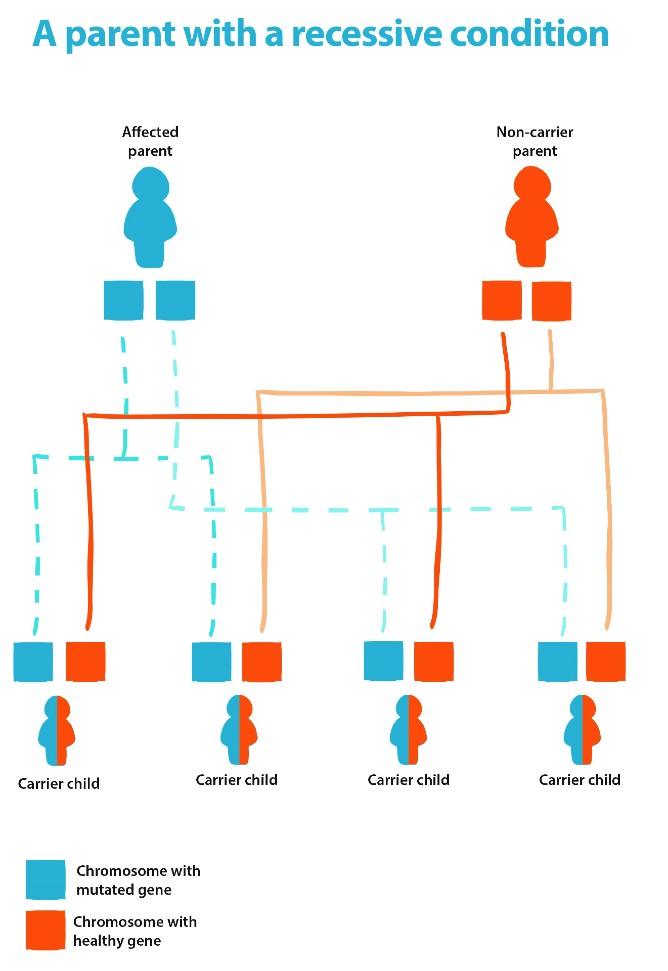
Parents with autosomal recessive conditions will pass on one copy of the changed gene to their children – as shown in the diagram below. It is very unlikely their children will be affected (unless the other parent is a blood relative).
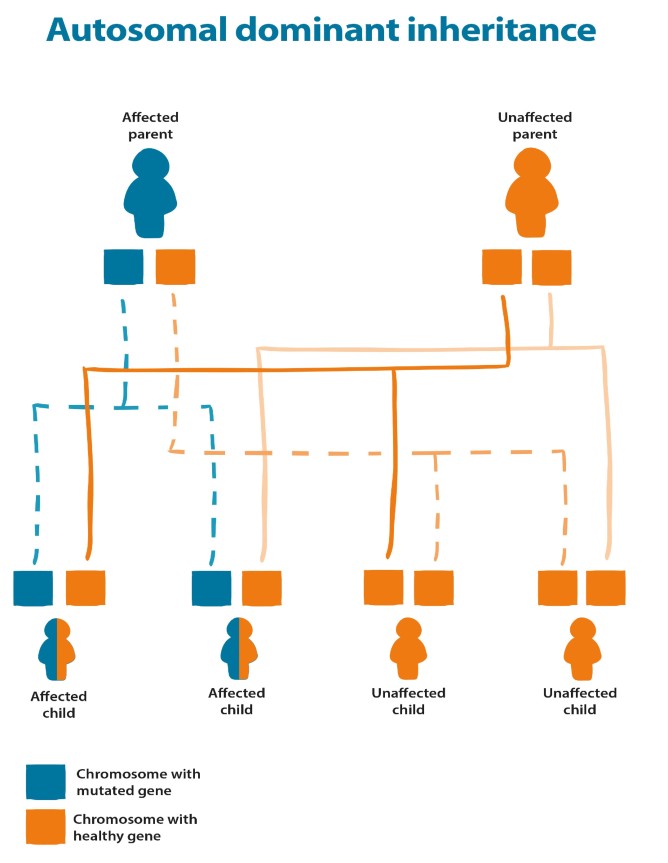
Autosomal dominant inheritance
Autosomal dominant inheritance includes, but is not limited to:
- Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD)
- Myotonic dystrophy
- Most oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophies
- Type 1 limb girdle muscular dystrophies
‘Autosomal’ means the change is in a gene on the non-sex chromosomes, so either sex can inherit the condition.
‘Dominant’ means the change has to occur in only one copy of the gene for someone to inherit the condition.
If one parent has the condition and the other doesn’t, as shown in the diagram below, there is a:
- 50 percent chance that each child will have the condition
- 50 percent chance that each child will be unaffected.
There are several specialist genetic centres throughout the country that do genetic tests and can offer advice. Your GP can arrange a referral to a clinical geneticist or genetic counsellor at your local genetics centre.
We’re here to support you
Webinars, Information Days, and support groups for our muscle wasting community. Our life-changing support is here for you.
Advice for living with or caring for someone with a muscle wasting condition.