Many muscle wasting conditions are caused by genetic changes. This means they can pass down a family from generation to generation. How this happens depends on the condition you or your family has.
How muscle wasting conditions are inherited
Learning about genetics and inheritance can help you understand more about your diagnosis and how it can be managed. If you’re thinking about starting a family or having more children, it can also help you understand the possible chances of your children being affected.
You may want to read this page with our information about your muscle wasting condition.
Speak to your GP or consultant if you have any worries or questions about inheritance and genetic testing. They can refer you to your local genetic counsellor or neurogenetics clinical service. This is a health professional who provides support, information, and advice about genetic conditions and genetic testing.
What are DNA, chromosomes and genes?
DNA contains the body’s genetic information. Inside our cells, DNA is organised into structures called chromosomes, which are inside the nucleus of each cell. Genes are small sections of DNA that contain instructions for the cells.
Think of your DNA as a recipe book and your genes as the recipes. Our cells use these (genetic) recipes to make proteins, which have lots of roles in the body.
Almost all our cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes, so 46 in total. These include:
- one pair of sex chromosomes – XX for females, XY for males
- 22 pairs of non-sex chromosomes, called autosomes
Sex chromosomes determine biological sex. Autosomes carry the rest of our genetic information.
For each pair of chromosomes, we inherit one from our mother and one from our father.
Small amounts of DNA are stored in other structures in the cell, called mitochondria. We only inherit mitochondrial DNA from our mother.
What is a genetic change?
A genetic change is a change in the DNA instructions.
This can happen by chance, for example if the cell makes a ‘mistake’ when it makes copies of its DNA. Our environment can also sometimes lead to genetic changes.
Our cells usually notice any changes and correct them, but they sometimes miss some changes.
Most changes do not harm our health. But some can affect how genes make proteins. This can result in a genetic condition such as muscular dystrophy.
Muscle wasting conditions pass through families in different ways or patterns. This depends on the type of condition and which gene has changed. They can be:
- X-linked recessive
- Autosomal recessive
- Autosomal dominant
- Inherited from the mother, through mitochondrial DNA
Sometimes a new genetic change can cause a muscle wasting condition in someone with no family history of the condition.
X- linked recessive inheritance
X-linked recessive inherited conditions include:
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)
- Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD)
- Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD)
- X-linked myotubular myopathy (XLMTM)
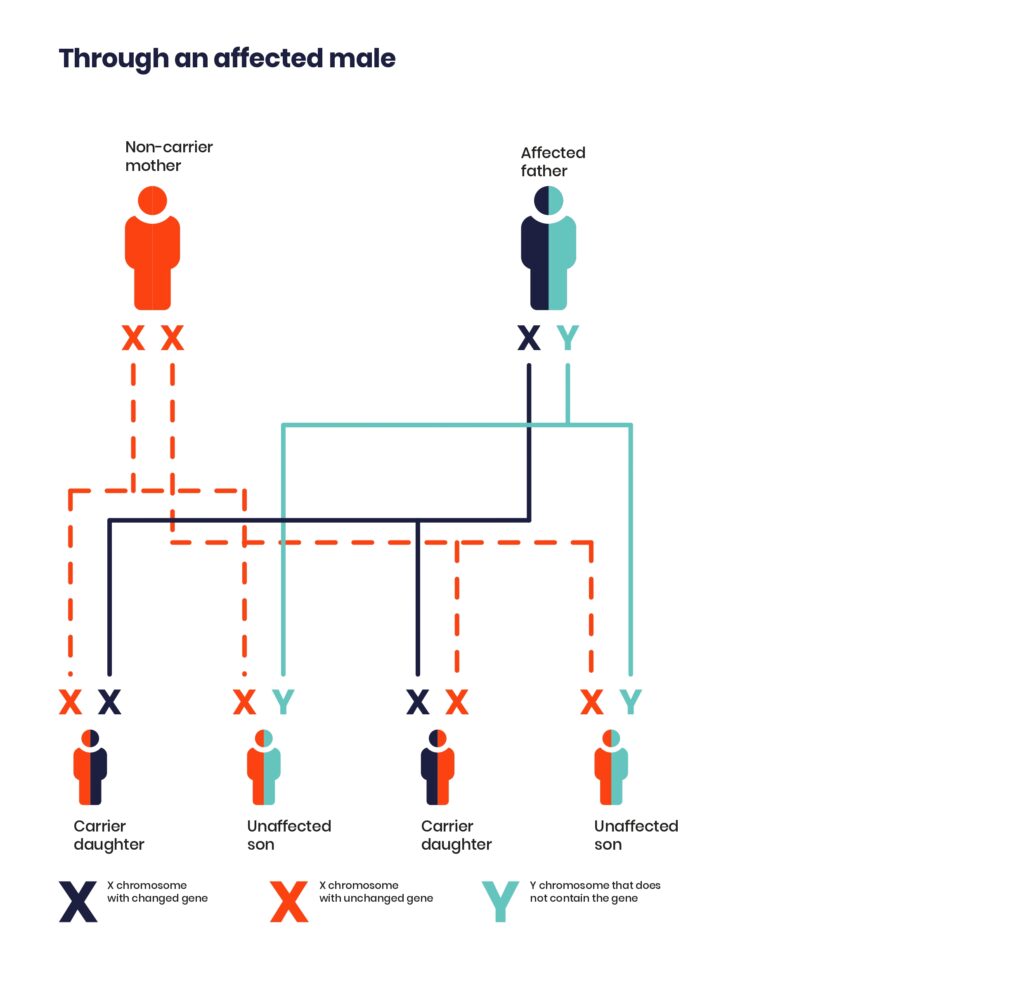
These conditions are caused by a change in a gene on the X chromosome, which is one of the sex chromosomes. Males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome; females have two X chromosomes.
If a male’s X chromosome has the changed gene, they will have the condition. They have only one copy of the gene because they have only one X chromosome.
If a female has the changed gene on one of their X chromosomes, there is still an unchanged copy of the gene on the other X chromosome. This makes them a ‘carrier’. They will not usually have symptoms of the condition but can pass the genetic change on to their children.
If a female carrier has children with an unaffected male, there is a:
- 1 in 2 chance that each son will have the condition
- 1 in 2 chance that each daughter will be a carrier
Each child has the same chance of being affected. For example, if this couple has two sons, each son will have a 1 in 2 chance of inheriting the condition.
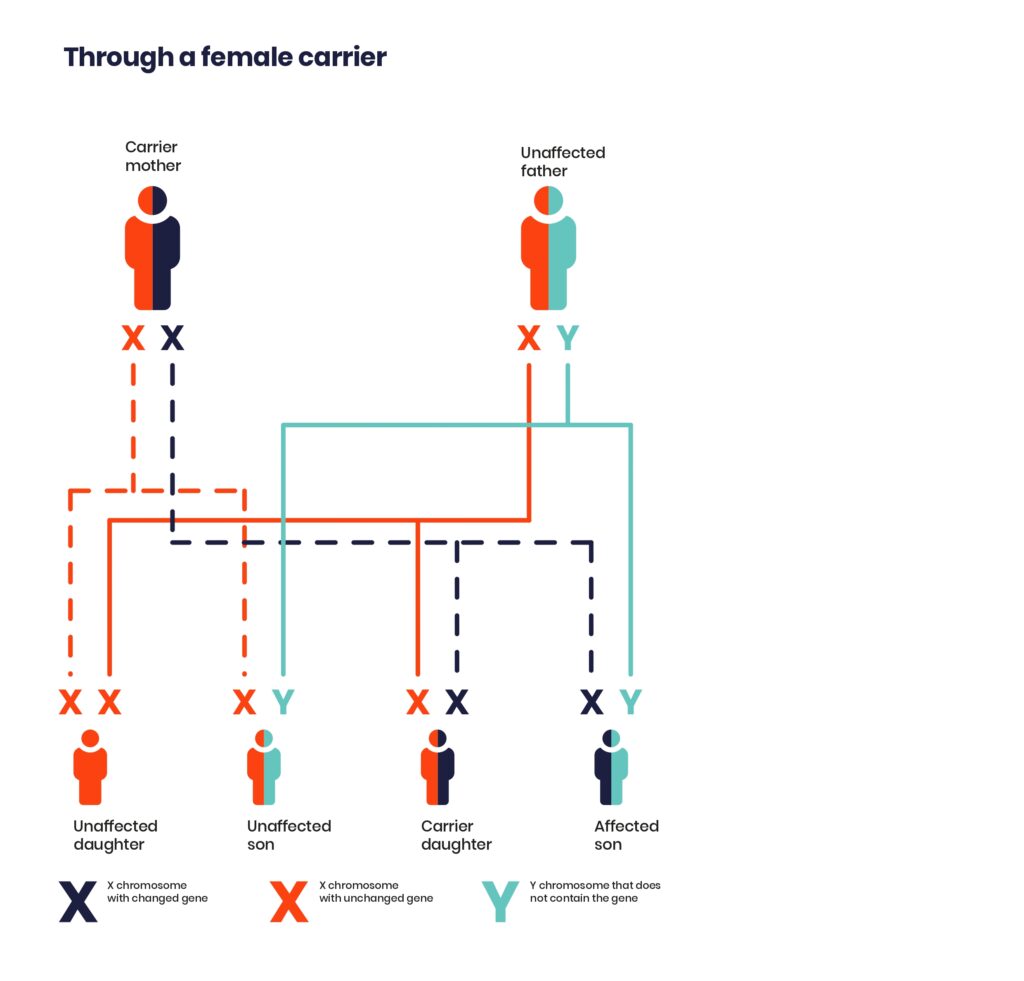
Unaffected males cannot pass on an X-linked condition. Males with an X-linked condition cannot pass it to their sons, but all their daughters will be carriers.
Autosomal recessive inheritance
Autosomal recessive inherited conditions include:
- Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA)
- Some limb girdle muscular dystrophies (LGMD)
- Some congenital muscular dystrophies (CMD)
‘Autosomal’ means the changed gene is on one of the autosomes (non-sex chromosomes). Male and female children can inherit the condition from both male and female parents.
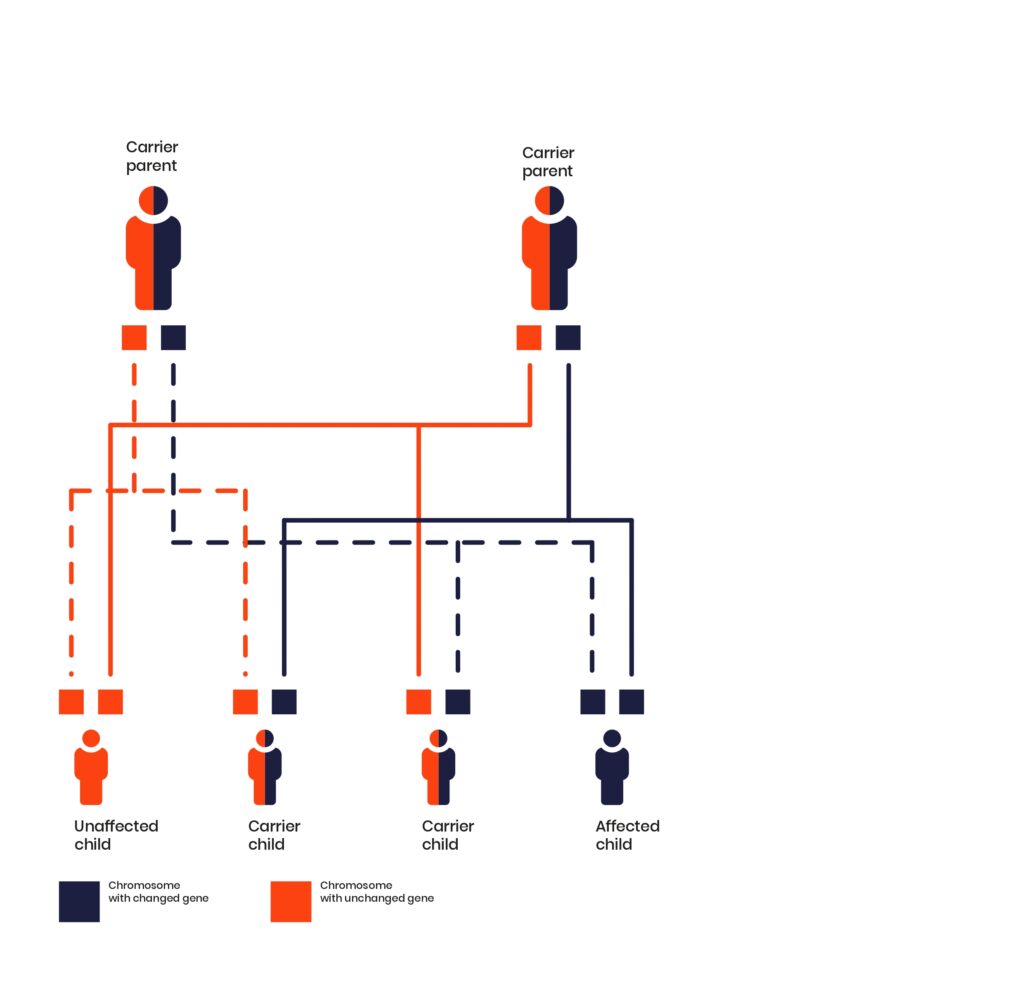
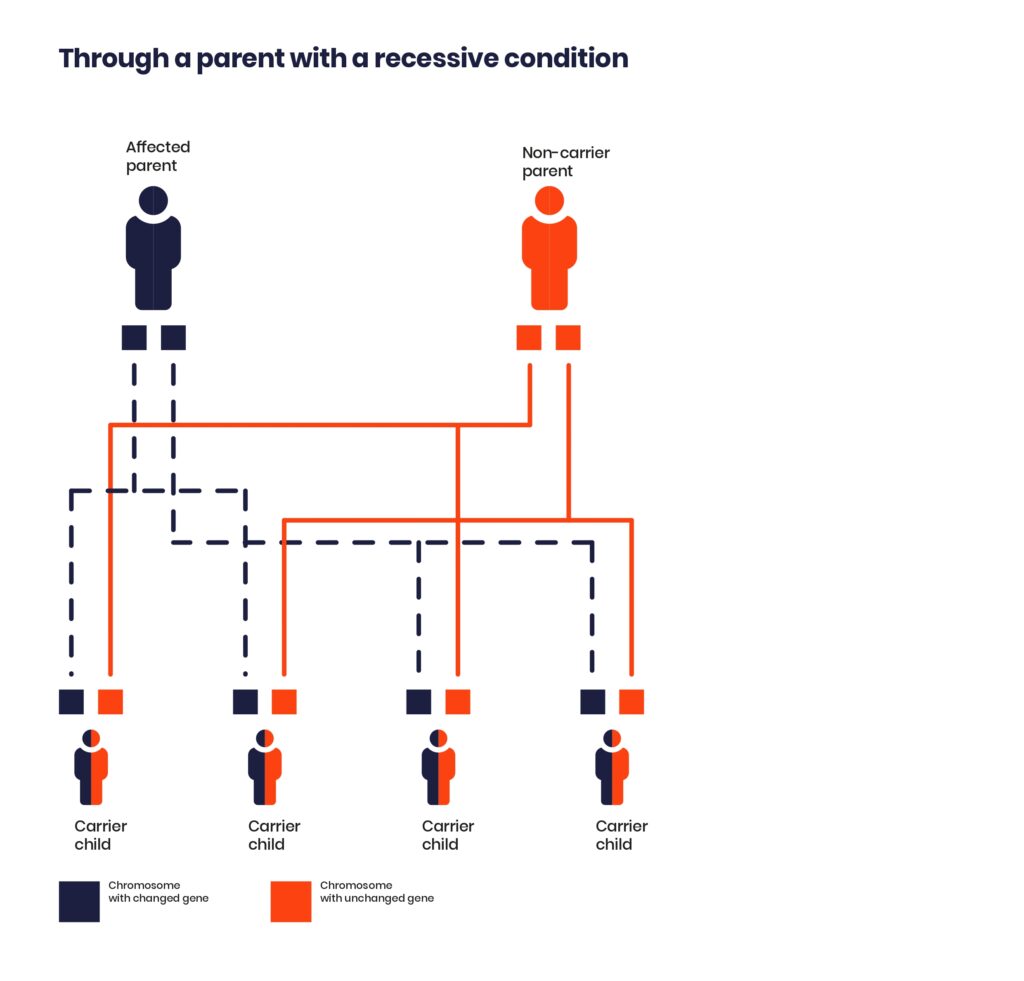
‘Recessive’ means a child will only have the condition if they inherit the changed gene from both parents. If they inherit the changed gene from just one parent, they will be a carrier and have no symptoms.
If the parents are both carriers, there is a:
- 1 in 4 chance that each child will be unaffected and not carry the change
- 1 in 2 chance that each child will be unaffected, but will be a carrier
- 1 in 4 chance that each child will have the condition
A parent with an autosomal recessive condition will pass on one copy of the changed gene to their children. It is unlikely their children will be affected, unless the other parent is a blood relative.
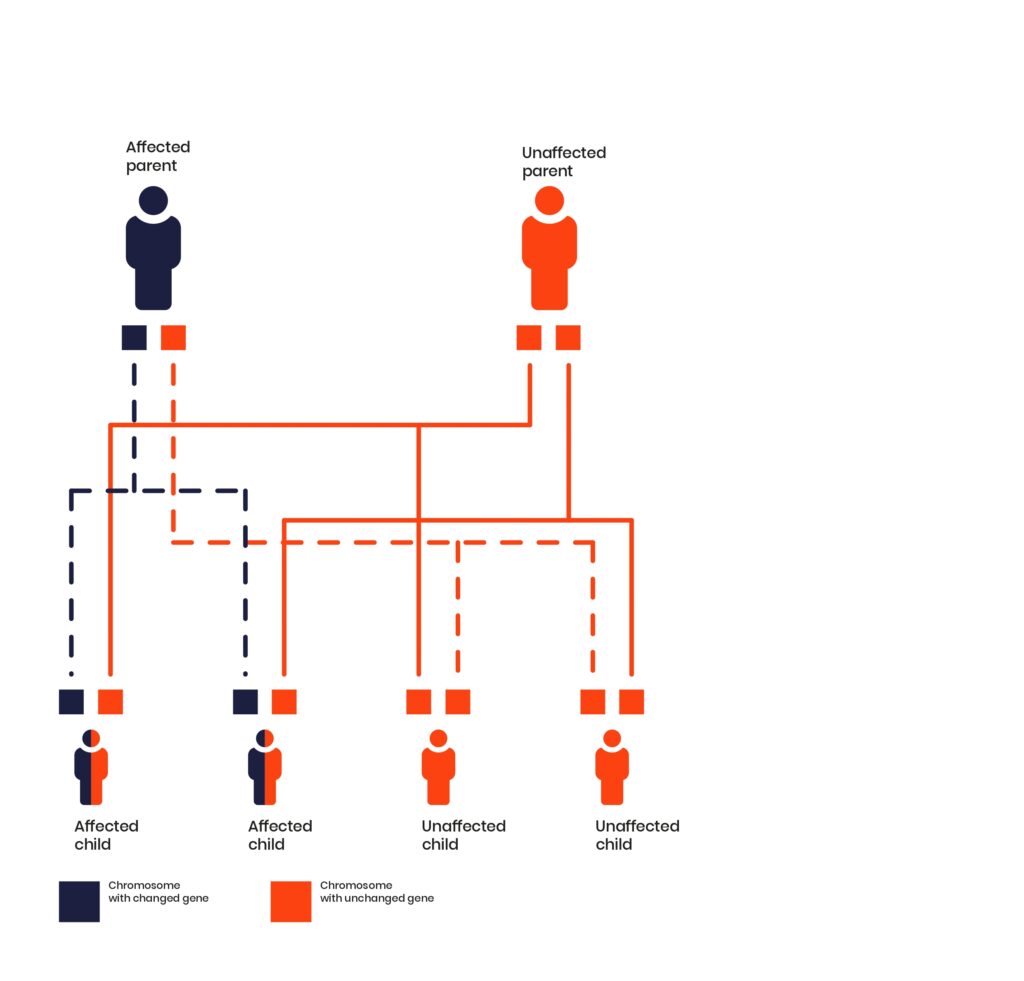
Autosomal dominant inheritance
Autosomal dominant inherited conditions include:
- Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD)
- Myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) and type 2 (DM2)
- Most oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophies (OPMD)
- Some limb girdle muscular dystrophies (LGMD)
‘Autosomal’ means the changed gene is on one of the autosomes (non-sex chromosomes). Male and female children can inherit the condition from both male and female parents.
‘Dominant’ means someone only needs to inherit one copy of the changed gene to have the condition.
If one parent has the condition and the other does not, there is a:
- 1 in 2 chance that each child will have the condition
- 1 in 2 chance that each child will be unaffected
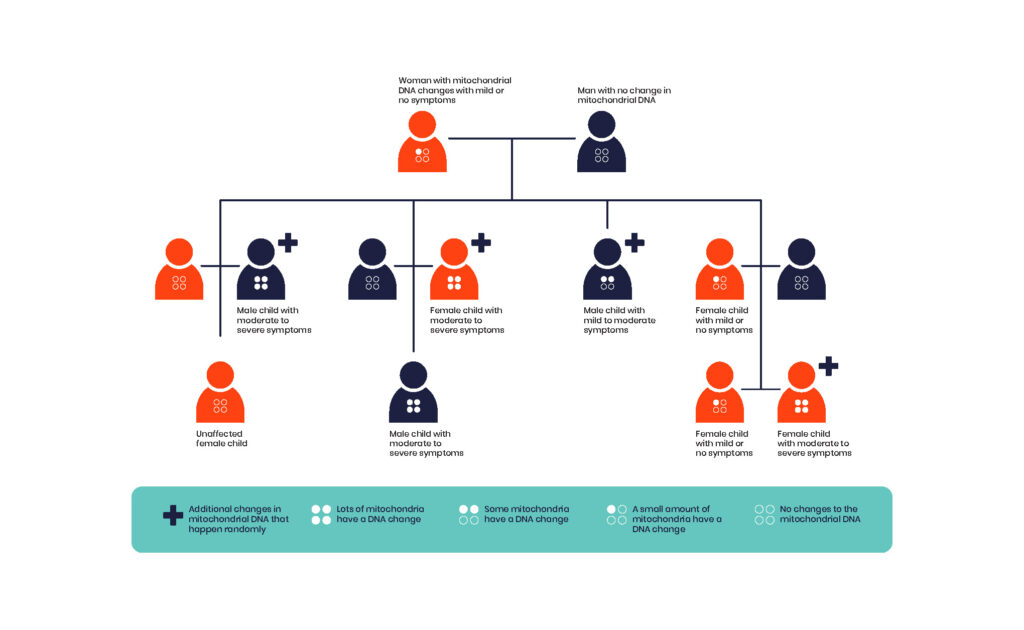
Mitochondrial inheritance
Mitochondria are small structures inside cells, which make energy for cells to work. Most of our cells have hundreds of mitochondria.
Mitochondria have their own DNA, which is separate from the DNA in the nucleus. A changed gene in the DNA from mitochondria or the nucleus can cause mitochondrial disease.
Often, a gene will only be changed in some of the mitochondria. If a small number of mitochondria have the changed gene, it is unlikely to cause a problem. But if most, or all, of the mitochondria in a cell have the changed gene, it can affect how the cell works. If enough cells are affected, it can cause a mitochondrial condition.
We inherit mitochondrial DNA from only our mother. In general, if the changed gene is in a mother’s mitochondrial DNA, they will pass it on to all their children. But this can depend on how many mitochondria in the mother’s egg has the changed gene. If most of the mitochondria have the changed gene, they will pass to the child, causing a mitochondrial condition. This can happen even if the mother has only mild symptoms or no symptoms.
Genetic centres throughout the UK offer genetic testing and advice. Your GP can refer you to your local centre. Genetic Alliance UK have a list of genetic services in the UK.
Genetic testing can:
- Help diagnose a muscle wasting condition
- Help your doctors manage your condition
- Show whether someone is a carrier of a muscle wasting condition
- Give information about how likely it is that other family members are affected and the risks of having affected children
- Help you find out whether any clinical trials are suitable for you
- Check for some muscle wasting conditions during pregnancy or In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF)
Genetic testing is not always quick or simple. It can take time to get results, and sometimes tests may not give a clear answer straight away. You may need more than one type of test over time. For some people, getting a clear diagnosis can take a long time, especially with rare or less understood conditions.
If you need support, you can get in touch with us for advice and information.

Author: Muscular Dystrophy UK
Reviewers: Prof Darren Monckton and Prof Henry Houlden
Last reviewed: May 2025
Next review due: May 2028
We’re here to support you
Webinars, Information Days, and support groups for our muscle wasting community. Our life-changing support is here for you.
Advice for living with or caring for someone with a muscle wasting condition.